Maybe you knew there was a possibility that it could happen. Maybe your partner's mother or father had dementia, and perhaps even their siblings, so you were watching for the signs. Or, maybe, it came out of the blue, and you never thought that dementia would ever impact you or your family.
When you start to notice changes in memory, behavior, and judgment that are not normal with your partner, it gives you a sinking feeling, whether you may have been expecting it or not.
Warning Signs of Dementia
According to the Alzheimer's Association, there are ten early warning signs of Alzheimer's and Dementia that you can be watching for:
1. Memory Loss That Disrupts Daily Life
Forgetting recently learned information, forgetting important dates or events, asking the same questions repeatedly, and increasingly needing to rely on memory aids or family and friends for things they used to handle on their own are all signs.
2. Challenges in Planning or Solving Problems
This may involve changes in the ability to follow a plan or work with numbers. For instance, they may have trouble following a familiar recipe or keeping track of monthly bills. They may have difficulty concentrating and/or taking longer to do things than they did before.
3. Difficulty Completing Familiar Tasks
Examples include having trouble driving to a familiar location, organizing a grocery list, or remembering the rules of a favorite game.
4. Confusion With Time or Place
This may involve losing track of dates, seasons, or the passage of time, trouble understanding something if it is not happening immediately, and possibly forgetting where they are or how they got there.
5. Trouble Understanding Visual Images and Spatial Relationships
Some people experience vision changes that may lead to difficulty with balance or trouble reading. This may also lead to difficulty judging distance and determining color or contrast, causing issues with driving.
6. New Problems With Words in Speaking or Writing
This often presents as difficulty following or joining a conversation. They may stop during a conversation and have no idea how to continue or repeat themselves. Moreover, they may struggle to find the right words.
7. Misplacing Things and Losing the Ability To Retrace Steps
They may put things in unusual places, lose things, and be unable to go back over their steps to find them again or accuse others of stealing, especially as the disease progresses.
8. Decreased or Poor Judgment
Experience in changes in judgment or decision-making. For example, when dealing with money or keeping themselves clean.
9. Withdrawal From Work or Social Activities
Because of the changes in the ability to hold or follow a conversation, many people experiencing changes due to dementia may withdraw from hobbies, social activities, or other engagements.
10. Changes in Mood and Personality
This shows up as being confused, suspicious, depressed, fearful, or anxious. They may be easily upset at home, with friends, or when out of their comfort zone.
If You Suspect Your Partner Has Dementia...
Don't ignore the signs. Schedule an appointment with your partner's primary care physician immediately to seek a diagnosis and take the next steps.
If there is a dementia diagnosis, you are likely completely overwhelmed. Your world has been turned upside down, and it is likely hard to think beyond each day at a time, let alone the next month or year. However, taking steps to plan ahead can help things go more smoothly for you and your entire family.
As the disease progresses, things are likely only to become more hectic, making it even more difficult to think clearly. Getting your legal, financial, and end-of-life planning finalized early on will make it easier for you to make the necessary decisions and communicate those decisions to the right people before things get even harder.
Legal
Ensure your partner has updated legal documents in place (if they don't already) before they are designated as unable to make those designations/decisions for themselves due to their new diagnosis.
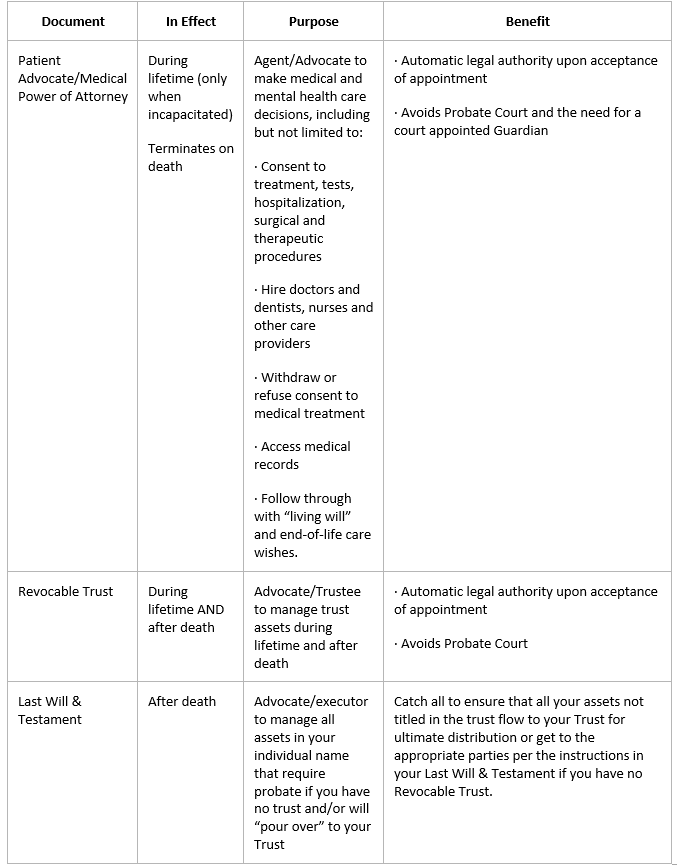
Patient Advocate/Health Care Durable Power of Attorney: This names someone as a "proxy" to make medical decisions for someone when they are not able to.
Living Will: This informs medical professionals of how one wants to be treated at the end of life (dying, permanently unconscious, etc.) and cannot make decisions on their own.
A Do Not Intubate, or DNI, order: This lets medical staff know someone does not want to be put on a breathing machine.
A Do Not Resuscitate, or DNR, order: This lets medical staff know not to perform CPR or other life-saving procedures in case the heart or breathing stops.
General Durable Power of Attorney: This names someone as a "proxy" to make financial decisions and handle financial transactions for someone when they are not able to.
Will: This names someone to be the executor to handle their estate after they are deceased.
Trust: For some, a Revocable or Irrevocable Trust naming someone to handle assets on their behalf and for their benefit either during their lifetime or after death is appropriate.
Financial Planning
It is important to work with your financial adviser to make sure fiscal affairs are for several reasons:
Make sure that all your financial records are accounted for using a Personal Recording Keeping document. Keep it in a safe place before that information is lost or forgotten by either or both partners.
Work with your financial adviser to make sure you have planned well to provide for your financial future, including your now more certain long-term care needs, including dementia care.
Ensure assets are positioned and titled properly to assist with future long-term care needs and any future resources and assistance that may be needed.
Research any insurances you may currently hold to make sure you understand how they may be used for future long-term care needs.
Talk about how you might want to handle future care needs for your partner with dementia. If that includes you, as the healthy spouse, taking time from work (if you are not yet retired), plan for how you will handle that financially. Planning ahead for how care will be funded is a key piece of future planning.
Research community and professional resources in your area. Put together a team to help you when needed.
Communicate your future plan to your family so that they can help you execute it when things are more hectic, and the disease is more difficult to deal with.
End-Of-Life
There is currently no cure for Alzheimer's disease or any other dementia. Some treatments, though, can manage some of the symptoms for a time.
However, a person who has been diagnosed will gradually decline, and the condition itself (or combined with additional health problems) will eventually result in death. For that reason, it is also important to plan ahead and make decisions for end-of-life early on.
Making sure the important legal documents are in place is the first step. Communicating preferences for end-of-life to important family members is the second step. If there are any preferences for end-of-life services, that should be documented. Using a Letter of Last instruction document is a good idea.
When your partner is diagnosed with dementia, it can be a shock. For many, it can be so overwhelming that it can be hard to breathe, let alone get your head around doing anything. But once the numbness wears off, lean on your financial adviser and professional team of advisers to get a plan in place so that the legal, financial, and end-of-life pieces are in order so that you can concentrate on caring for your partner and their ongoing needs.
 Contributed by: Sandra Adams, CFP®
Contributed by: Sandra Adams, CFP®