Contributed by: Robert Ingram
Contributed by: Robert Ingram
The back-to-school season is right around the corner. And if you have school-aged children, the thought of planning for their college education may be enough to cause your own case of back-to-school jitters. Costs of a four-year education at many colleges and universities are already well into the six-figure range (per child!). For many families hoping to cover a large portion of the costs, significant savings goals are likely required. That’s why, more than ever, you should create a college savings plan as early as possible.
College Costs Keep Rising
When planning to fund an education goal that may be years away, focusing on today’s costs is (unfortunately) just the beginning. Like the prices of many other goods and services, college costs have increased over time. These costs, however, have been rising much faster than those of other household expenses. According to JPMorgan Asset Management’s research, tuition costs have grown by an average annual rate of 6.4% since 1983. At this rate, today’s cost of tuition would double in about 11 years. Even if this rate of inflation slowed somewhat, potential college costs are eye-opening.
The illustration below shows projected total tuition, fees, and room and board expenses for a four-year, public or private college education, with a 5% annual increase in costs.
Source: JPMorgan Asset Management College Planning Essentials, using The College Board, 2018 Trends in College Pricing. Future college costs estimated to inflate 5% per year. Average tuition, fees and room and board for public college reflect four-year, in-state charges.
As you can see in this example, a child who is 10 years old today could expect a total cost of $136,085 at an in-state public college or university. Her education at a private college could cost over $308,000.
The power of compound growth on your savings and invested earnings can be one of your best allies as you save for these potential future costs. Let’s say the family of our 10-year-old child began saving $3,600 each year. At 7% growth compounded annually, they would have $36,935 by the time she turned 18. What if, instead, they began saving that same amount eight years earlier, when the child was age 2? At the same 7% annual return, they would have $100,396. The sooner you can begin saving and investing, the more time compounding has to work its magic.
The Burden of Student Loan Debt
As the costs of college have continued to rise, the amount of student loan debt has grown as well. A recent report from the New York Federal Reserve Consumer Credit Panel showed that outstanding student loan debt totaled $1.44 trillion as of September 30, 2018. In addition, studies from the Institute of College Access and Success found that 65% of students graduating in 2017 from public and private, non-profit colleges had student loans, and the average borrower owed $28,650.
Loans can help provide students the funds to complete their educations, but a large debt balance can have serious implications for a graduate’s personal finances. As new graduates begin their careers, servicing this student loan debt can take up a large portion of their budgets. More dollars going to pay down debt means fewer dollars available for other needs, for building an emergency fund, saving for a house, or saving for retirement. (Click here to see some financial tips for new graduates). Parents managing student loan debt can also feel similar constraints. Often, parents in the home stretch toward retirement are paying down debt instead of funding their own retirement plans.
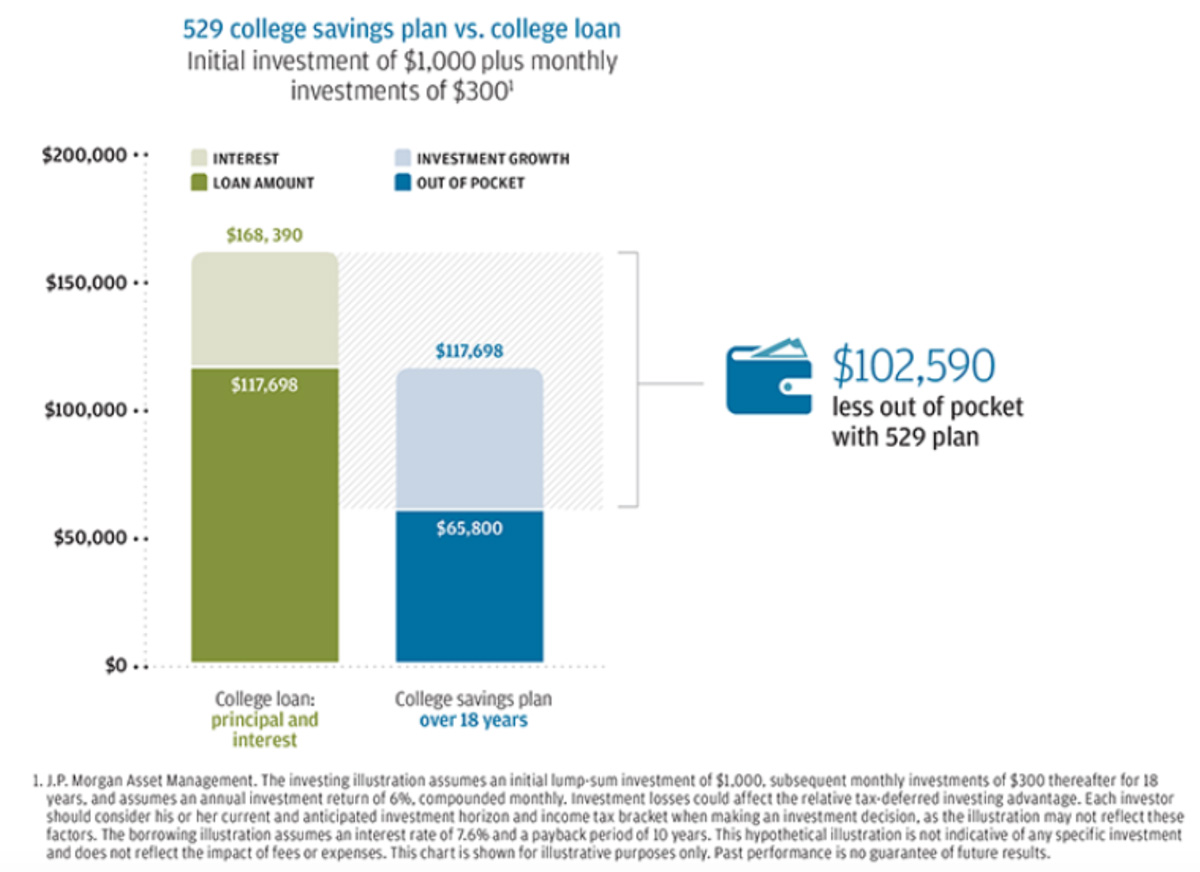
Of course, every dollar of college expenses paid from savings can mean one less dollar of debt to service. More than that, the longer you have to build college savings, the greater the difference between the out-of-pocket cost of paying for college with debt and the out-of-pocket cost of saving. Take a look at the following chart, which compares the cost of funding education through loans (the principal borrowed and interest) with the cost of saving over 18 years.
In this hypothetical example, the total out-of-pocket amount of $65,800 contributed to the savings plan combined with investment earnings of 6% annually provided the total balance of $117,698. Borrowing that same $117,698 could result in total spending of $168,390 for the loan principal and interest.
What about Financial Aid?
If you’re like many clients thinking about college planning, you may be concerned that your savings and investments will negatively affect your eligibility for college aid. You might be worried that the more you save, the less likely it is that you will receive assistance.
To determine financial aid eligibility, schools use an Expected Family Contribution (EFC), which is a measure of a family’s financial strength. The EFC formula takes into account the incomes and assets of both the student and the parents. While the amount of savings and investment assets are considered, assets – and particularly those held in parents’ names – are a much smaller factor than incomes.
The EFC formula includes up to 50% of the student’s income and 47% of parents’ income. On the other hand, the EFC considers up to 20% of the student’s assets and only 5.64% of the parents’ non-retirement assets, above a protected amount. Although balances in college savings plans are counted along with other non-retirement assets, the smaller percentage applied to parental assets can allow parents to build some meaningful savings without drastically affecting their student’s EFC. For a closer look at the financial aid process, check out our college planning webinar.
As with other areas of financial planning, college savings involves balancing your goals and priorities in order to most effectively align your resources. Your own unique circumstances will determine the right amounts to save, and when and where to save. If we can be a resource for any of your college planning needs, please let us know!
Robert Ingram, CFP®, is a CERTIFIED FINANCIAL PLANNER™ professional at Center for Financial Planning, Inc.® With more than 15 years of industry experience, he is a trusted source for local media outlets and frequent contributor to The Center’s “Money Centered” blog.