Fall is upon us, but just around the corner is the 2021 Open Enrollment Period. The window to select next year’s benefits at your employer runs from Nov. 1st through Dec. 15th. In the past, you may not have given these selections much thought, but this year, the impact of COVID-19 may have you thinking about the many “What if...” situations. Like, “What happens if my family and I get sick?” or “What happens if I'm out of work for a long time?” Understanding your options helps ensure that you're taking full advantage of the insurance plans and other benefits. Here are 5 reasons you should review your benefits and coverages:
1. Do you have the right health insurance coverage?
Most employer health and wellness benefits have at least a couple of health insurance options, such as PPO or HMO plans. Today, available choices usually include a type of High Deductible Health Plan (HDHP) eligible for a Health Savings Account (HSA). With a higher deductible, you will be responsible for a greater amount of medical costs out-of-pocket before the insurance plan begins to pay (compared to a more traditional lower-deductible plan). In addition to the opportunity to contribute to an HSA, the higher deductible plans usually have lower premiums than plans with lower deductibles. However, you should focus on the total potential costs, including premiums, deductibles, co-pays, and annual out-of-pocket maximums.
When deciding which plan makes the most sense, you would normally consider your health history and the services you might expect to use. Generally, the greater your expected medical costs each year, the more likely you benefit from a lower deductible plan. You also should consider how you want to manage your health care (are you comfortable staying within a specific network of doctors and hospitals, or do you want greater flexibility?). Some health plans, for example, will require higher co-pays for services provided outside of their direct network.
The COVID-19 pandemic has made it even more important to understand your coverage options and make decisions accordingly. Some questions to ask when evaluating insurance plans could include:
If I get sick and need treatment, what restrictions does the plan have on services? What hospitals or outpatient facilities can I use?
Are there any deductibles waivers for COVID-related services or office visits?
How does prescription drug coverage handle any special treatments or therapeutics?
2. Do you need to add young adult children to your health insurance plan?
Under the Affordable Care Act, health plans that offer dependent child coverage must allow children to be covered under the parent’s family plan until they reach age 26. With the widespread disruptions in the economy, many young adults may have lost their employer coverage or face other cost-prohibitive options.
On plans that cover dependents, you can add your child under age 26 to your plan as a dependent even if he or she:
is not living with you
is not financially dependent on you
is married
is eligible to enroll in their own insurance plan
3. Strengthen your life insurance and disability insurance protections.
Employer benefit plans offering life insurance typically provide a basic amount of coverage at no additional cost to you, such as an amount equal to your base salary. Many plans will allow you to purchase additional coverage (supplemental life insurance) up to a maximum dollar amount or a multiple of your salary, for example, up to five times your salary.
Often there is additional spousal coverage you can purchase as well.
While the supplemental and spousal insurance has an extra cost that can increase as the employee/spouse ages, employer group insurance tends to be less costly than individual policies and can provide a good base of coverage. When considering your life insurance needs, here are some tips.
Many employers also provide a group disability insurance benefit. This can include short-term coverage (typically covering up to 90 or 180 days) and/or long-term disability (covering a specified number of years or up through a certain age such as 65). Disability benefits often cover a base percentage of income such as 50% or 60% of salary, many times at no cost with some plans offering supplemental coverage for an additional premium charge.
As with the life insurance benefits, group disability may not completely replace your lost income, but it can provide a solid foundation of coverage that you should maximize.
4. Your retirement plan (401k, 403b, etc.) might need a tune-up.
Start with contributions to your account.
Are you contributing up to the maximum employer match, if offered? Take advantage of free money!
Are you making the maximum annual contribution (elective deferral)? The basic limit was $19,500 in 2020.
If you can save more after maximizing your elective deferrals, does your plan offer separate after-tax contributions? This could be a way to leverage additional Roth IRA conversion opportunities.
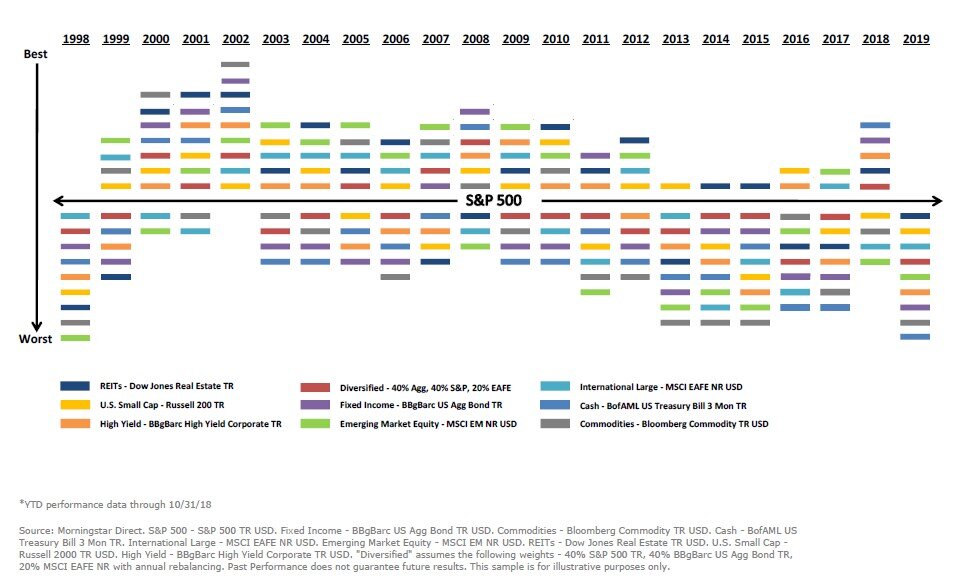
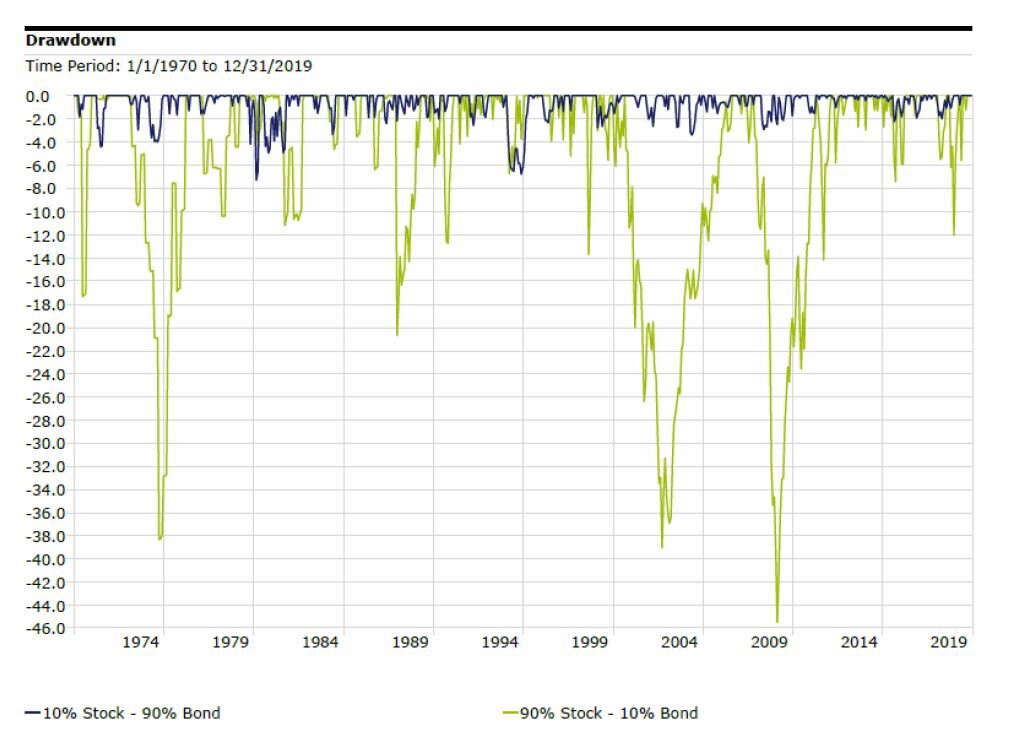
Review your investment allocation. Do you have the appropriate balance of stocks, bonds, cash, and other asset categories in your portfolio given your timeframe and tolerance for risk? After experiencing the plunging financial markets of March and the sharp rebound in the stock market through the summer, you may have concentrations in certain assets that are above or below your desired target. This could be a good time to rebalance your portfolio back to those targets.
5. Michigan’s auto insurance no-fault law changed in July.
Okay, while your auto insurance is probably not part of your employer group benefits, now would be a good time to review your auto insurance coverage along with your other benefits.
Earlier this July, legislation went into effect here in Michigan that changed the no-fault insurance law. One of the main changes related to Personal Injury Protection (PIP) is the part covering medical bills and lost wages if you are injured in an accident. Residents can now select different levels of PIP, whereas Michigan law had previously required insurance covering unlimited medical benefits for the lifetime of the injured person. Read more about the Michigan insurance reform.
If your policy has been renewed since July 1st, you may have chosen a specific PIP level or continued a default option for unlimited coverage. Selecting a lower level of PIP can lower your premiums depending on the limit you choose. However, it's important to note that carrying a higher level of protection could still make sense for many people and could be worth the extra cost.
Having a conversation with your insurance agent and financial advisor about the potential risks versus cost savings can help you decide if changes to your policy are appropriate.
As always, if we can be a resource for you, please let us know.
Robert Ingram, CFP®, is a CERTIFIED FINANCIAL PLANNER™ professional at Center for Financial Planning, Inc.® With more than 15 years of industry experience, he is a trusted source for local media outlets and frequent contributor to The Center’s “Money Centered” blog.